Pandas jest biblioteką Pythona służącą do analizy i manipulowania danymi
Podstawowe byty
Seria - Series
Ramka danych - DataFrame
import pandas as pd= pd.Series([3 , - 5 , 7 , 4 ])print (s)print ("values" )print (s.to_numpy())print (type (s.to_numpy()))print (s.index)print (type (s.index))
0 3
1 -5
2 7
3 4
dtype: int64
values
[ 3 -5 7 4]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=4, step=1)
<class 'pandas.core.indexes.range.RangeIndex'>
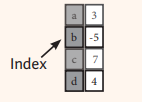
import pandas as pdimport numpy as np= pd.Series([3 , - 5 , 7 , 4 ], index= ['a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ])print (s)print (s['b' ])'b' ] = 8 print (s)print (s[s > 5 ])print (s * 2 )print (np.sin(s))
a 3
b -5
c 7
d 4
dtype: int64
-5
a 3
b 8
c 7
d 4
dtype: int64
b 8
c 7
dtype: int64
a 6
b 16
c 14
d 8
dtype: int64
a 0.141120
b 0.989358
c 0.656987
d -0.756802
dtype: float64
import pandas as pd= {'key1' : 350 , 'key2' : 700 , 'key3' : 70 }= pd.Series(d)print (s)
key1 350
key2 700
key3 70
dtype: int64
import pandas as pd= {'key1' : 350 , 'key2' : 700 , 'key3' : 70 }= ['key0' , 'key2' , 'key3' , 'key1' ]= pd.Series(d, index= k)print (s)= "Wartosc" = "Klucz" print (s)
key0 NaN
key2 700.0
key3 70.0
key1 350.0
dtype: float64
Klucz
key0 NaN
key2 700.0
key3 70.0
key1 350.0
Name: Wartosc, dtype: float64
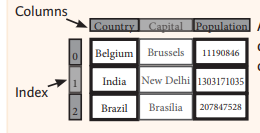
import pandas as pd= {'Country' : ['Belgium' , 'India' , 'Brazil' ],'Capital' : ['Brussels' , 'New Delhi' , 'Brasília' ],'Population' : [11190846 , 1303171035 , 207847528 ]}= pd.DataFrame(data)print (frame)= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['Country' , 'Population' , 'Capital' ])print (data2)
Country Capital Population
0 Belgium Brussels 11190846
1 India New Delhi 1303171035
2 Brazil Brasília 207847528
Country Population Capital
0 Belgium 11190846 Brussels
1 India 1303171035 New Delhi
2 Brazil 207847528 Brasília
import pandas as pd= {'Country' : ['Belgium' , 'India' , 'Brazil' ],'Capital' : ['Brussels' , 'New Delhi' , 'Brasília' ],'Population' : [11190846 , 1303171035 , 207847528 ]}= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['Country' , 'Population' , 'Capital' ])print ("Shape:" , df_data.shape)print ("--" )print ("Index:" , df_data.index)print ("--" )print ("columns:" , df_data.columns)print ("--" )print ("--" )print (df_data.count())
Shape: (3, 3)
--
Index: RangeIndex(start=0, stop=3, step=1)
--
columns: Index(['Country', 'Population', 'Capital'], dtype='object')
--
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3 entries, 0 to 2
Data columns (total 3 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Country 3 non-null object
1 Population 3 non-null int64
2 Capital 3 non-null object
dtypes: int64(1), object(2)
memory usage: 204.0+ bytes
--
Country 3
Population 3
Capital 3
dtype: int64
Ćwiczenia: (ex8.py)
Napisz kod, który utworzy serię z następującej listy liczb: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]. Wyświetl serię w formacie tabelarycznym:
Utwórz serię, gdzie kluczami będą miesiące ('Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar'), a wartościami odpowiednie temperatury: [0, 3, 5]. Wyświetl w formacie tabelarycznym:
Stwórz pustą ramkę danych z kolumnami Product, Price, Quantity, a następnie wypełnij ją danymi:
Apple
1.2
10
Banana
0.5
20
Orange
0.8
15